
Japanese Verb Basics Part 1 Verb Groups & the Masu Form
Furthermore, we also talked about Japanese verbs, ru-verbs in particular. In Japanese, there are two main verb types called "ru-verbs" and 'u-verbs." In this article, we are going to learn about how these two verb types behave in casual and polite forms in positive and negative sentences. Additionally, there are also two irregular verbs.

Chart Ru verbs by LazHiral on DeviantArt Japanese Language, Verb, User Profile, Just Giving
Japanese verbs can be roughly divided into two categories: Ru verbs and U verbs (and there are two irregular verbs.) In Japanese, all verbs end in the sound Ru or U. Ru verb examples: Mi ru, Tabe ru, or Ne ru U verb examples: Nom u, Kik u or Hanas u; Ru verbs. To conjugate Ru verbs, you must drop the syllable Ru (る) and add the formal form of.

Japanese Verb Groups Uverbs, Ruverbs, Irregular verbs Lesson 36 YouTube
The conjugation rule for the past-negative tense of verbs is pretty much the same as all the other negatives that end in 「ない」. You simply take the negative of any verb, remove the 「い」 from the 「ない」 ending, and replace it with 「かった」. To change verbs into the past-negative tense. Change the verb to the negative and.

Week 4 Japanese Verbs (ruverbs, kuru and suru) YouTube
Japanese verb groups: Ru-Verbs / V2. Ru verbs or V2 verbs end in any kana in the い (i)/え (e) column + る (ru). This is why sometimes ru-verbs are also known as iru-verbs and eru-verbs. Because the base of the verb stays the same when it's conjugated, these verbs are called 一段 いちだん 動詞 どうし ("one-form verb").

Japanese Verbs Uverbs, Ruverbs and Conjugation
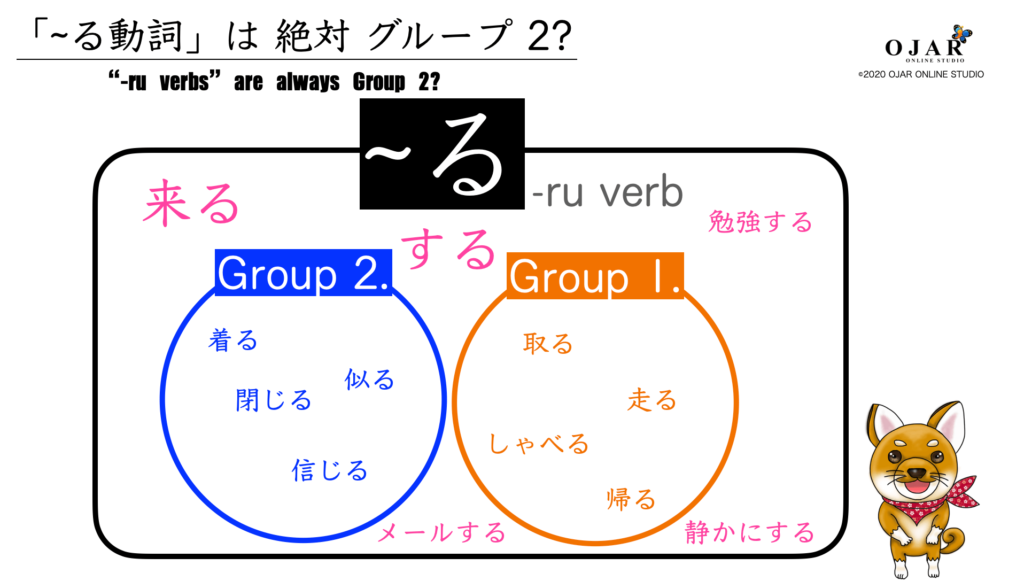
Here's a tip to help you separate the true ru verbs versus the false ones. When the verb has an iru ( いる ) or eru ( える ) ending, it is truely a ru verb. For example, a verb like okiru ( おきる ) ( 起きる ) (to get up) is a true ru verb because it has the iru ending. However let's look at the verb naoru ( なおる ) ( 直る.
Japanese Lesson 14 Verbs (with fully clear illustrations) OJAR ONLINE STUDIO
Japanese Verbs Categories. Japanese verbs are classified into three groups: Group 1 (-いる and - えるverbs), Group 2 (-る verbs) and lastly Group 3 (irregular verbs. All these three groups are differentiated by the ending of the verb. Group 1 Japanese Verbs (or Ichidan Verbs) Verbs in this group are ended by -いる and - える.

Japanese Verbs Conjugation Chart
Japanese verbs always contain two parts: a verb base and a suffix. Grammatically, verb bases are called "stems." In the above example: 見 み る, the stem is "mi" and the suffix is "ru" and then they become the plain form. This is the reason why 見 み る is categorized into ru-verbs. *There are some terms to call this verbs: Ichidan verbs, V verbs, and Group II.

The Passive Form Japanese Verbs and 〜られる
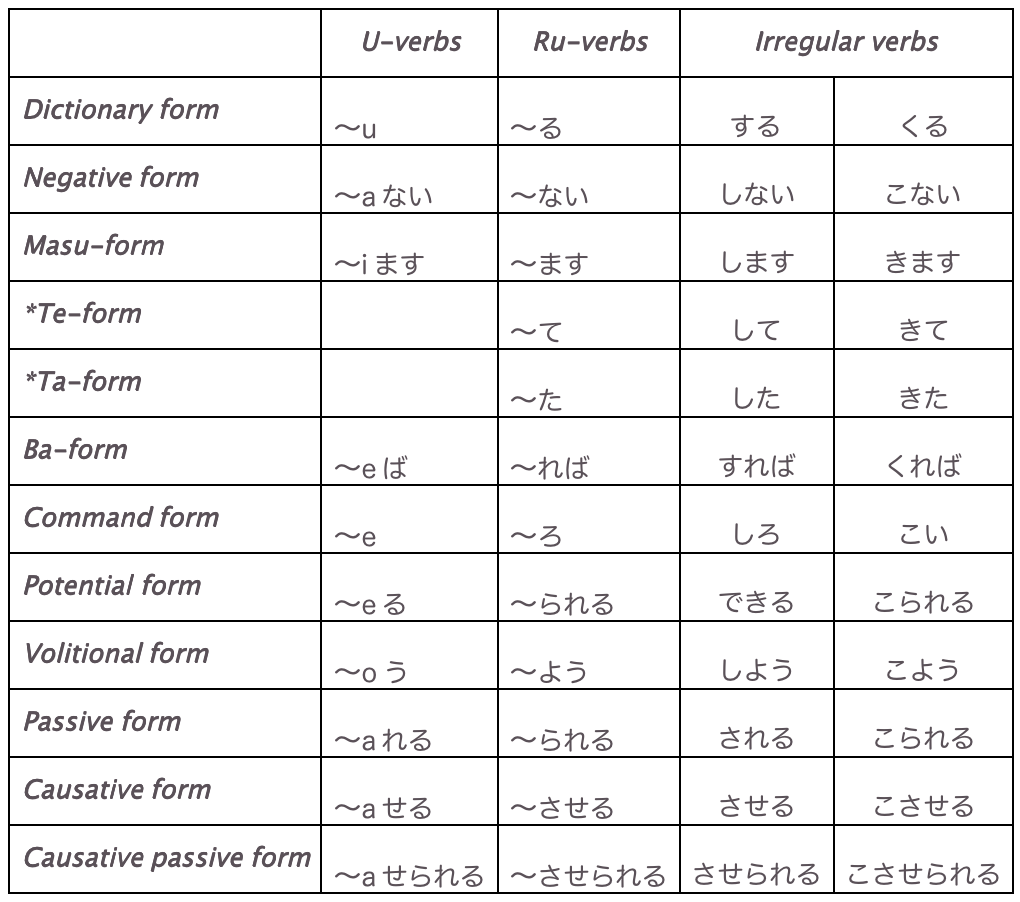
Basic Verb Conjugation. There are three categories of verbs in Japanese: ru -verbs, u -verbs, and irregular verbs. Ru and u verbs follow regular conjugation: There are only two irregular verbs in Japanese: する and くる. They are cojugated as follows: Ru -verbs are so called because you add the suffix ru to the verb base to form the.

Informal past tense for ruverbs Basic japanese words, Japanese verbs, Learn japanese words
Japanese verbs conjugate to express tenses, to connect with other phrases, and to show various nuances. Compared to other languages, Japanese conjugation types can be a bit more complicated. There are many different verb forms as well as polite forms. The conjugations can even be combined together! Ru-verbs, U-verbs, and Irregular Verbs

【GENKI L3】る RU or う U Verb How to figure out Japanese verb groups YouTube
言う 【い・う】 (u-verb) - to say. 言い出す 【い・い・だ・す】 (u-verb) - to start talking. In order to conjugate all u-verbs and ru-verbs into their respective polite forms, we will first learn about the stem of verbs. This is often called the masu-stem in Japanese textbooks but we will call it just the stem because it.

Japanese verb conjugation RU japaneselessons Palabras japonesas, Vocabulario japones
Download Ru-verb conjugation list. -ru verbs are formed by adding - ru to the end. In addition to that, as you can see from above examples, -ru verbs that end in " - iru " or " - eru ".

Japanese Verbs Conjugation Chart for Beginners Etsy Ireland
There are u-verbs that end in ru however. The way to tell ru-verbs and u-verbs that end in ru apart is to look at the vowel sound preceding the ending ru. If there is an i or e before the ru it is a ru-verb. If the ru is proceeded by any other vowel, the verb is an uverb. Here are some examples of う verbs: よむ- To read かく- To write.

JAPANESE VERB CONJUGATION (RU VERBS CONJUGATION) YouTube
食べる - 「べ」 is an e-vowel sound so it is a ru-verb. 分かる - 「か」 is an a-vowel sound so it is an u-verb. If you're unsure which category a verb falls in, you can verify which kind it is with most dictionaries. There are only two exception verbs that are neither ru-verbs nor u-verbs as shown in the table below.
italki The basics you need to know about Japanese verb conjugation
The next group of verbs we'll look at is ichidan verbs. Examples of these verbs include 見る (mi ), "to see," 起きる (oki ), "to wake up," 開ける (ake ru ), "to open," and 食べる (tabe ru ), "to eat." These verbs are called "る-verbs" in many Japanese textbooks because they all end in the hiragana character る.

Japanese Verbs Conjugation Chart
Japanese verb conjugation basics. 1. Ru verbs. These are verbs that end in -iru and -eru. Examples of this are miru (みる), which means "to look" and taberu (たべる), which means "to eat". 2. Irregular verbs. Thankfully, there are only two irregular verbs in Japanese! The 2 irregular Japanese verbs are suru (する), meaning.

Japanese UVerbs Learn japanese words, Japanese language, Study japanese
1. Verb Groups: Different Types of Japanese Verbs. Japanese verbs always end with u or ru, and verbs are categorized into three groups: Class 1: U-verb; Class 2: Ru-verb; Class 3: Irregular verb; As the conjugation system itself is very simple, memorizing the patterns and rules will help you learn how to use Japanese verbs properly.